Base mode
Correction output#
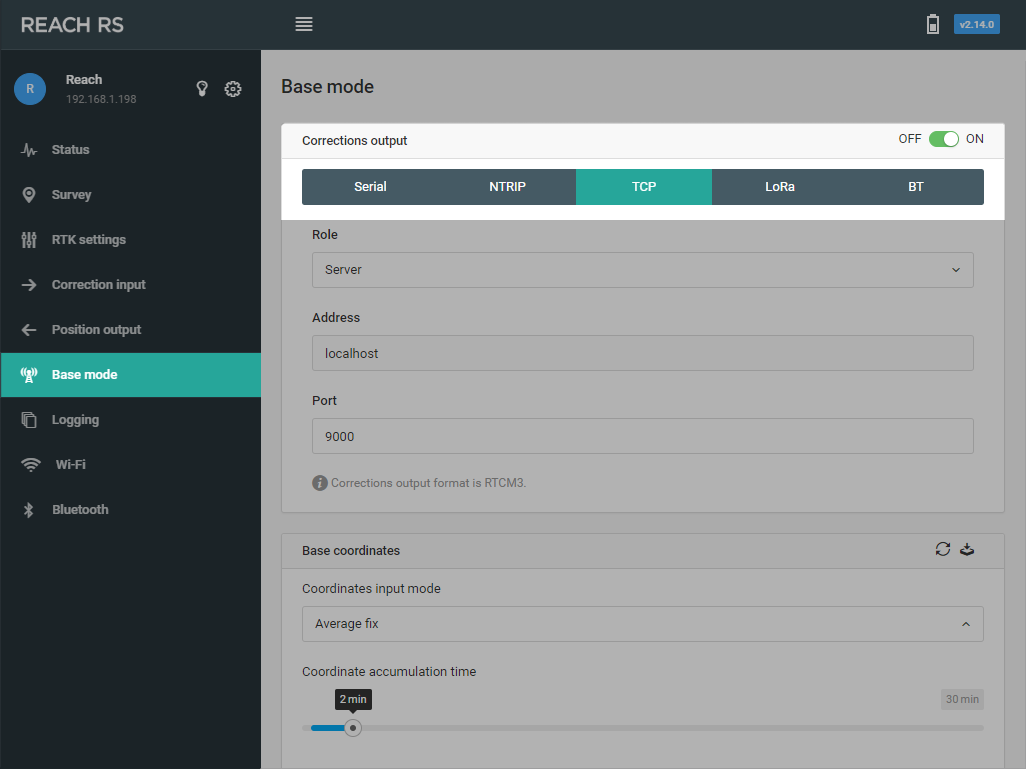
Reach outputs correction in industry standard RTCM3 format. Correction data can be sent via Serial, TCP, NTRIP, or LoRa for Reach RS/RS+.
Serial#
Serial port connection is available through several hardware connection options. All of them support the following baud rates: 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200.
UART#
Corresponds to TTL UART on Reach module or to RS232 port on Reach RS/RS+ extension connector. Common way to connect to radio to send correction data.
USB-to-PC#
When connected over USB to a PC, Reach will show up as several devices, one of them will be a serial port. You can use this serial port to send correction data to the PC.
USB OTG#
Use a micro-USB OTG cable to connect USB accessories. In this mode, only USB devices that emulate a serial port could be used. Examples of popular chips that are supported: FT232, CP2102. There are numerous devices built on these chips that will provide you a TTL UART or RS232 port.
NTRIP#
NTRIP is an industry standard way of transferring GNSS corrections over the Internet, with Reach Panel you can use any public service or your own private caster. NTRIP does not support point-to-point communication, e.g. you can not use it to transfer corrections from one Reach to another directly. In NTRIP terminology, there are servers, clients and a caster. Server sends correction to the caster, and clients can receive them by connecting to that caster.
In order to send correction to NTRIP caster, you need to know:
- IP address or domain name of the caster
- Port
- Password
- Mount point
When connecting via NTRIP in base mode, Reach acts as an NTRIP server.
TCP#
A typical scenario for using TCP is sending correction data to an application on the same network or to a server with a public IP.
note
Ports below 3000 are reserved for internal use only.
TCP supports two roles:
Server#
You need to specify port and after that clients will be able to connect to this device on it’s IP address. Many clients can be connected to the same server.
Client#
You need to specify an IP address of the server and port number.
If Reach Panel does not allow to set a certain port number, it means that it is reserved for internal use.
LoRa Radio#
Reach RS/RS+ has an internal LoRa radio which is used for receiving or sending corrections. For Reach M+, external LoRa radio is available, it can be connected via USB or S1/S2 port. The radio works only in one way, it could either be configured to send corrections (on base) or to receive them (on rover). Using LoRa modulation, it is possible to hit up to 19km (11.8 miles) in line of sight or a few km in urban areas with just 20 dBm power output. As long as frequency and air rate settings match, an unlimited number of rovers can listen for correction from the same base.
The lower the air rate is, the longer the working distance will be. Depending on your RTCM3 messages selection, Reach Panel will automatically block insufficient air rates. Disable correction messages or reduce rate in order to unlock lower air rates. Air rate on transmitting Reach and on receiving must match.
Make sure to select appropriate output power and frequency according to your local regulations.
Bluetooth#
You can use Bluetooth for correction output. Note that you cannot set both position output and base correction output to Bluetooth at the same time.
RTCM3 messages#
The minimal subset that is required for RTK to function is 1002 message for 1Hz with GPS observations and 1006 message for 0.1Hz with base station antenna position. Enabling more messages or higher rates requires higher connection bandwidth.
| RTCM3 messages | Message type |
|---|---|
| Minimal required messages | |
| 1002 | GPS L1 observations |
| 1006 | ARP station coordinate |
| Optional messages for other GNSS | |
| 1010 | GLONASS L1 observation |
| 1097 | Galileo MSM7 |
| 1107 | SBAS MSM7 |
| 1117 | QZSS MSM7 |
| 1127 | BeiDou MSM7 |
Here is some information about each message from RTCM STANDARD 10403.31:
Message types 1002 and 1010 contain L1 RTK GPS and GLONASS raw satellite data, respectively. GPS 1002 message is mandatory to use due to the RTKLIB code. You could turn on GLONASS 1010 message if you want to use this GNSS.
Message type 1006 provides the earth-centered, earth-fixed (ECEF) coordinates of the antenna reference point (ARP) for a stationary reference station and the height of the ARP above a survey monument. It is the second mandatory message to turn on after GPS 1002.
Messages 1097 (GALILEO), 1107 (SBAS), 1117 (QZSS), 1127 (BeiDou) are MSM7 (Multiple Signal Messages). MSM7 are high resolution messages that provide the same information for each GNSS system: pseudorange, phase-range, doppler, SNR. That means that you should turn on only one message of the chosen system to get all data about it.
tip
Remember that you can not use GLONASS and BeiDou systems together.
Base position#
tip
Check the Placing the base guide to learn about different ways to set up your base.
There are two main options for how to specify base station position. Note that RTK positioning is relative to the base station, so any inaccuracy in its position will result in a constant shift of rover coordinates. For many applications, it is not critical, and averaged single coordinate of the base could be used. If your application requires absolute accuracy for rover position an accurate base coordinate must be entered.
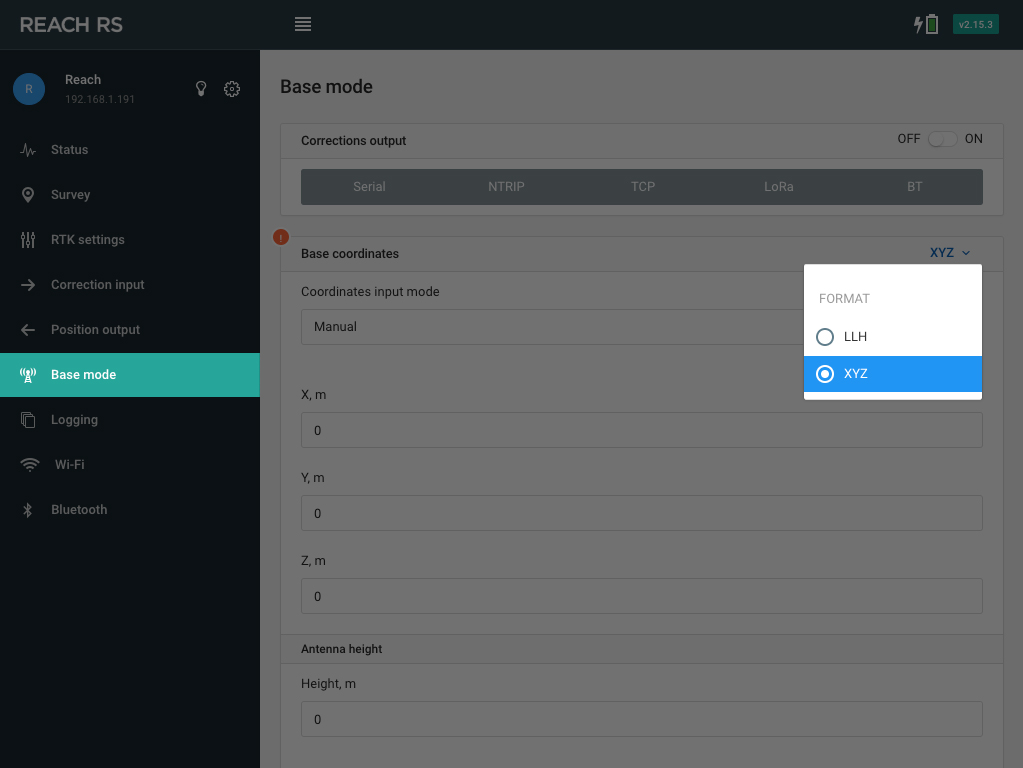
Manual#
In this mode you supply a coordinate known a priori by locating the unit above the surveyed point. Coordinate has to be supplied in ECEF XYZ or in WGS84 Latitude and Longitude and WGS84 ellipsoid height. Antenna height offset is entered at this stage as well, offset is limited to 6.5535 m (21.5 feet) by the RTCM message.
You can change the position format in the top right corner of the Base coordinates frame.
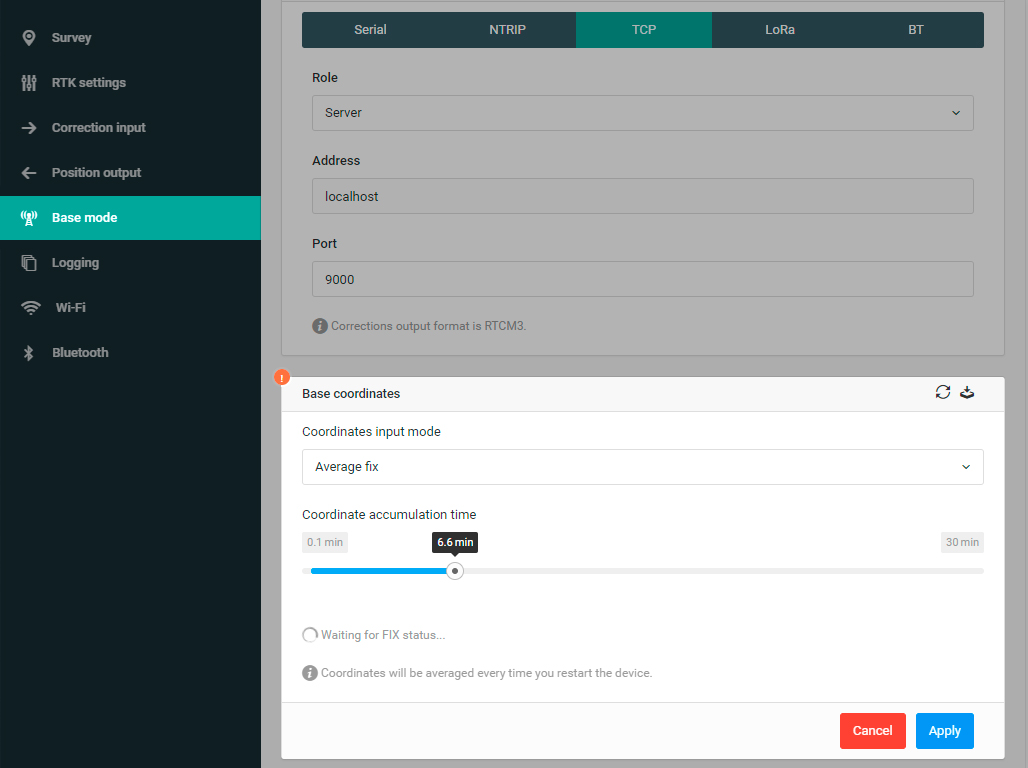
Average#
By default, Reach will average base position every time it starts. This feature significantly simplifies the initial setup in a new location. However, it will not provide an accurate absolute coordinate.
Reach Panel has a unique feature that allows it to determine base station position while working as a rover from another base. This is done by obtaining RTK Fixed solution, averaging it over a period of time and this way obtaining an accurate position for the base. A typical scenario would involve setting up a local base station by determining its coordinate from NTRIP and then broadcasting correction locally, thus reducing the baseline for rovers and improving positioning performance.
If the reference station is too far away, it is possible to average float and still improve the accuracy of the position.
In case no correction is available when setting up base or absolute accuracy is not required, averaged single coordinates could be used.
Save averaged position to manual
After you have successfully obtained averaged position, you might want to save it for future use. Click on the Save coordinates icon and position will be saved as if it was entered in manual mode. Now every time Reach starts it will broadcast this position in correction messages.
Repeat averaging
If you would like to restart base position averaging process you can click on the Repeat averaging icon. This is especially useful in a situation when you accidentally moved Reach during averaging.
1: Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services. 2016. RTCM STANDARD 10403.3 DIFFERENTIAL GNSS (GLOBAL NAVIGATION SATELLITE SYSTEMS) SERVICES – VERSION 3. Virginia: Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services, pp. 108-262