Position output
Formats#
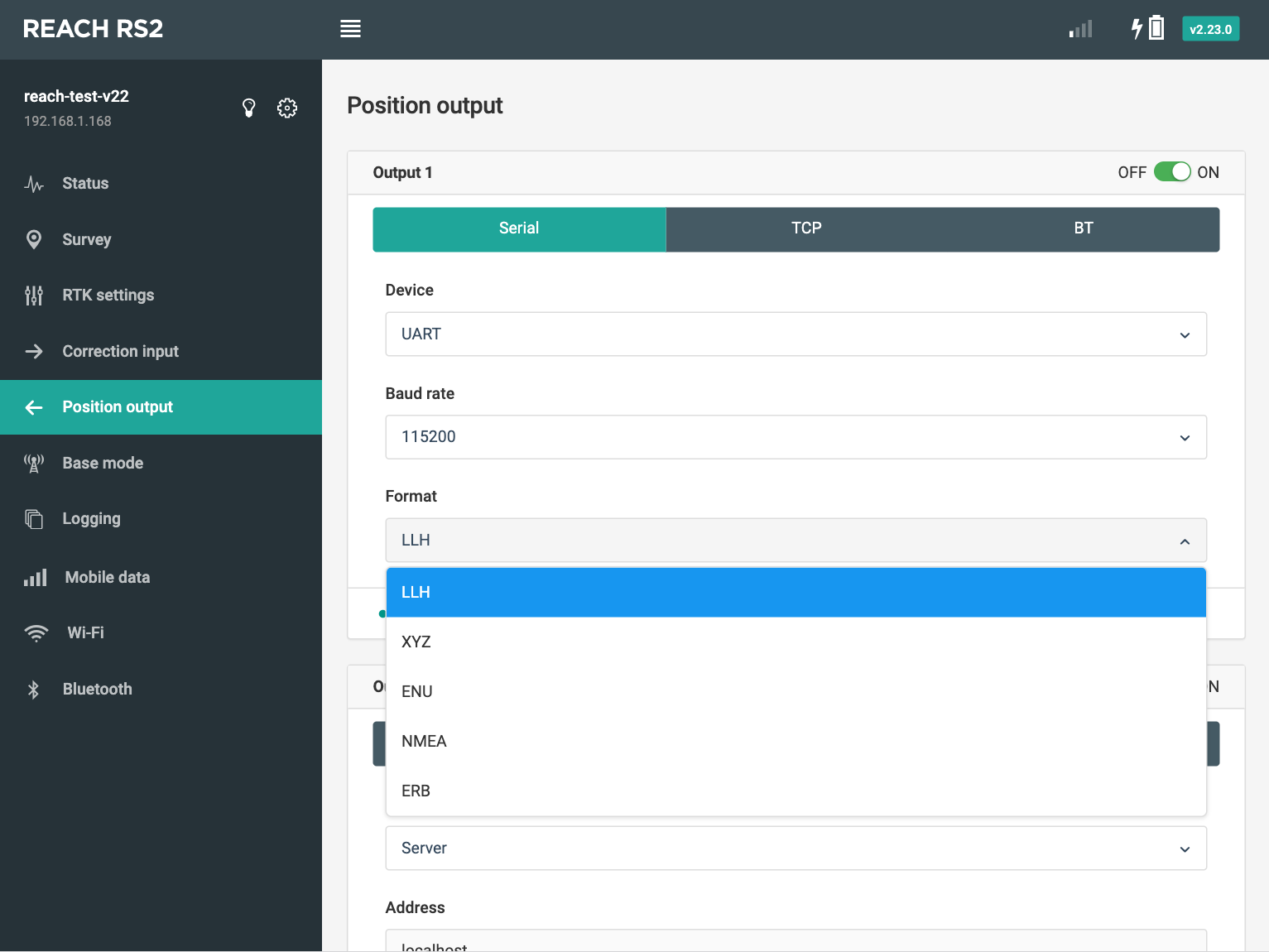
Reach RS/RS+ supports the following position output formats:
LLH#
Simple text protocol for Latitude, Longitude, and Height as well as solution status. Protocol definition can be found in RTKLIB ver. 2.4.2 Manual [PDF, 6.1 MB] on page 102.
XYZ#
Simple text protocol for X, Y, Z ECEF coordinates as well as solution status. Protocol definition can be found in RTKLIB ver. 2.4.2 Manual [PDF, 6.1 MB] on page 102.
ENU#
Simple text protocol for East, North and UP components of the baseline as well as solution status. Protocol definition can be found in RTKLIB ver. 2.4.2 Manual [PDF, 6.1 MB] on page 102.
NMEA 0183#
The most popular standard in the industry. Supported messages are GGA, GSA, GST, GSV, RMC, VTG, ZDA. When NMEA output is enabled, Reach can output its position to third-party devices, equipment, or vehicles. You can change Talker ID from GP to GN, select the required messages, and set the output rate.
Check the protocol definition in RTKLIB ver. 2.4.2 Manual [PDF, 6.1 MB] on page 102.
ERB#
note
ERB format is deprecated.
Used for communication to Ardupilot, you can find protocol description in this document [PDF, 202 KB].
Data in any of these formats can be sent via Serial, TCP, or Bluetooth.
Serial#
Serial port connection is available through several hardware connection options. All of them support the following baud rates: 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, 230400.
UART#
Corresponds to RS232 port on Reach RS/RS+ extension connector. Common way to connect to autopilot or another consumer of position data.
USB-to-PC#
When connected over USB to a PC, Reach RS/RS+ will show up as several devices, one of them will be a serial port. You can use this serial port to send position data to the PC.
USB OTG#
Use a micro-USB OTG cable to connect USB accessories. In this mode, only USB devices that emulate a serial port could be used. Example of popular chips that are supported: FT232, CP2102. There are numerous devices built on these chips that will provide you an RS232 port.
TCP#
Typical scenario for using TCP is sending position data to an application on the same network or to a server with a public IP.
note
Ports below 3000 are reserved for internal use only.
TCP supports two roles:
Server#
You need to specify the port, and after that, clients will be able to connect to this device on its IP address. Many clients can be connected to the same server.
Client#
You need to specify IP address of the server and port number.
If Reach Panel does not allow to set a certain port number, it means that it is reserved for internal use.
Bluetooth#
Bluetooth output is used to stream position data to smartphones, tablets, or data collectors. Please make sure to pair your device in Bluetooth settings.
note
iOS devices do not support getting a location over Bluetooth from third-party hardware.
You can learn more about getting Reach RS2 coordinates on Android via Bluetooth in this guide.