Correction input
Base correction#
Configuring correction is required if you want to go beyond standalone positioning. Reach supports corrections input in RTCM3 format, which is the most popular format in the industry. Data in this format can be received via Serial, TCP, NTRIP, Bluetooth, or LoRa for Reach RS/RS+.
Serial#
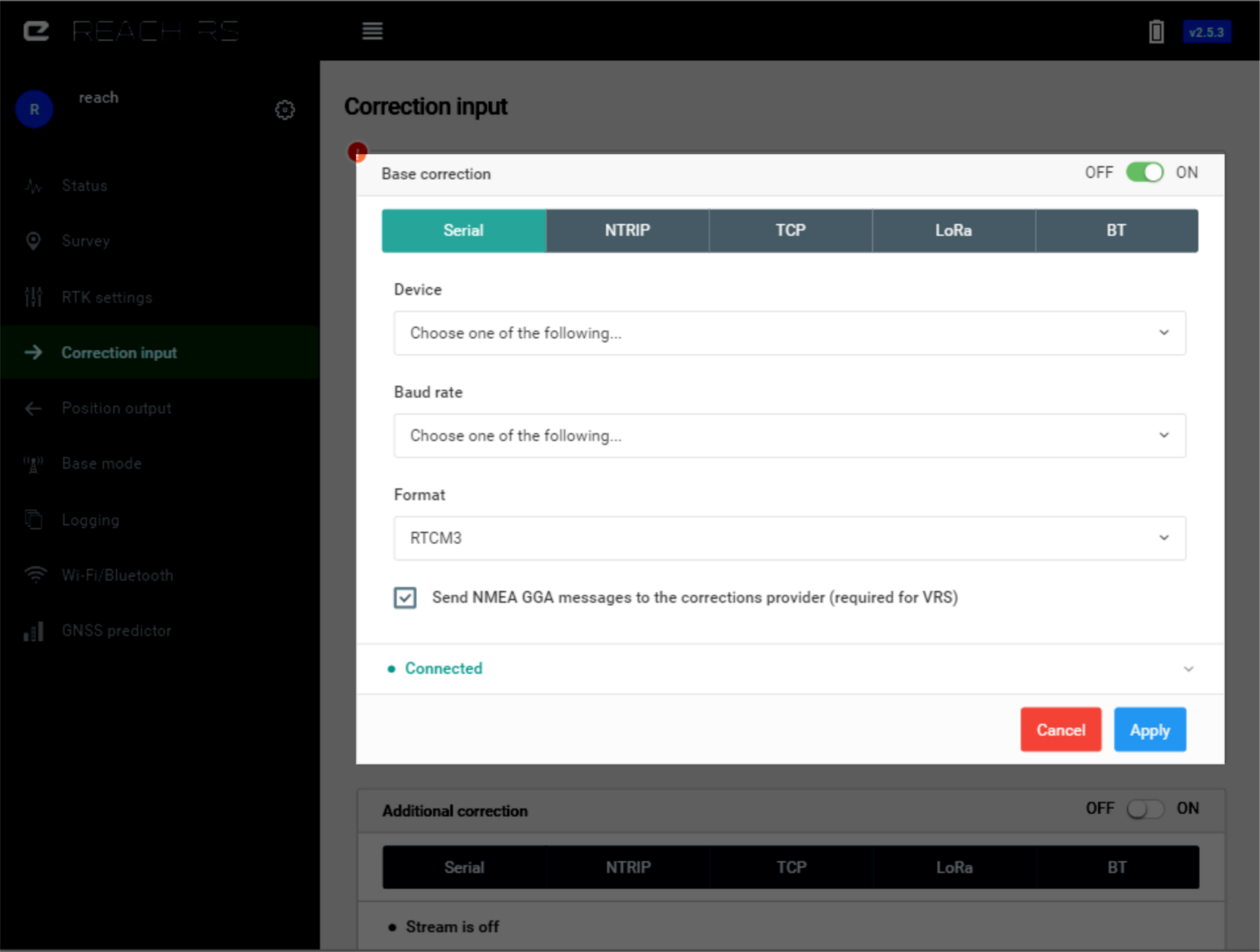
Serial port connection is available through several hardware connection options. All of them support the following baud rates: 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200.
UART#
Corresponds to RS232 port on Reach RS/RS+. Common way to connect radio or another device providing correction.
USB-to-PC#
When connected over USB to a PC, Reach will show up as several devices, one of them will be a serial port. You can use this serial port to send corrections to the device.
USB OTG#
Use a micro-USB OTG cable to connect USB accessories. In this mode, only USB devices that emulate a serial port could be used. Example of popular chips that are supported: FT232, CP2102. There are numerous devices built on these chips that will provide you a TTL UART or RS232 port. This is an easy way to connect radio modems as well.
NTRIP#
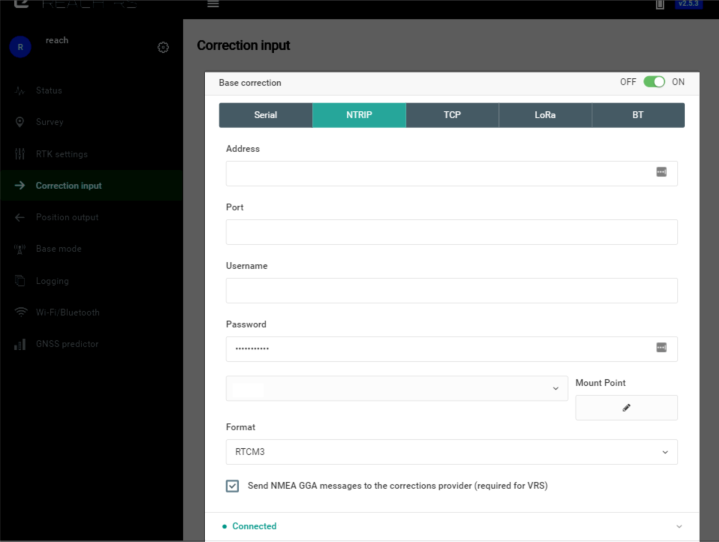
NTRIP is an industry-standard way of transferring GNSS corrections over the Internet, with Reach Panel you can use any public service or your own private caster. NTRIP does not support point-to-point communication, e.g. you can not use it to transfer corrections from one Reach to another directly. In NTRIP terminology, there are servers, clients, and a caster. Server sends correction to the caster, and clients can receive them by connecting to that caster.
In order to receive correction from NTRIP caster, you need to know:
- IP address or domain name of the caster
- Port
- Username
- Password
- Mount point
When connecting to a mount point that has VRS or nearest mount point feature, which automatically provides you with a connection to the closest base station, it is required to send your position back to the caster. Tick Send NMEA GGA messages to the corrections provider, and after Reach obtains single solution, it will start sending it to the caster.
Check out the guide guide to learn more about working with NTRIP service.
TCP#
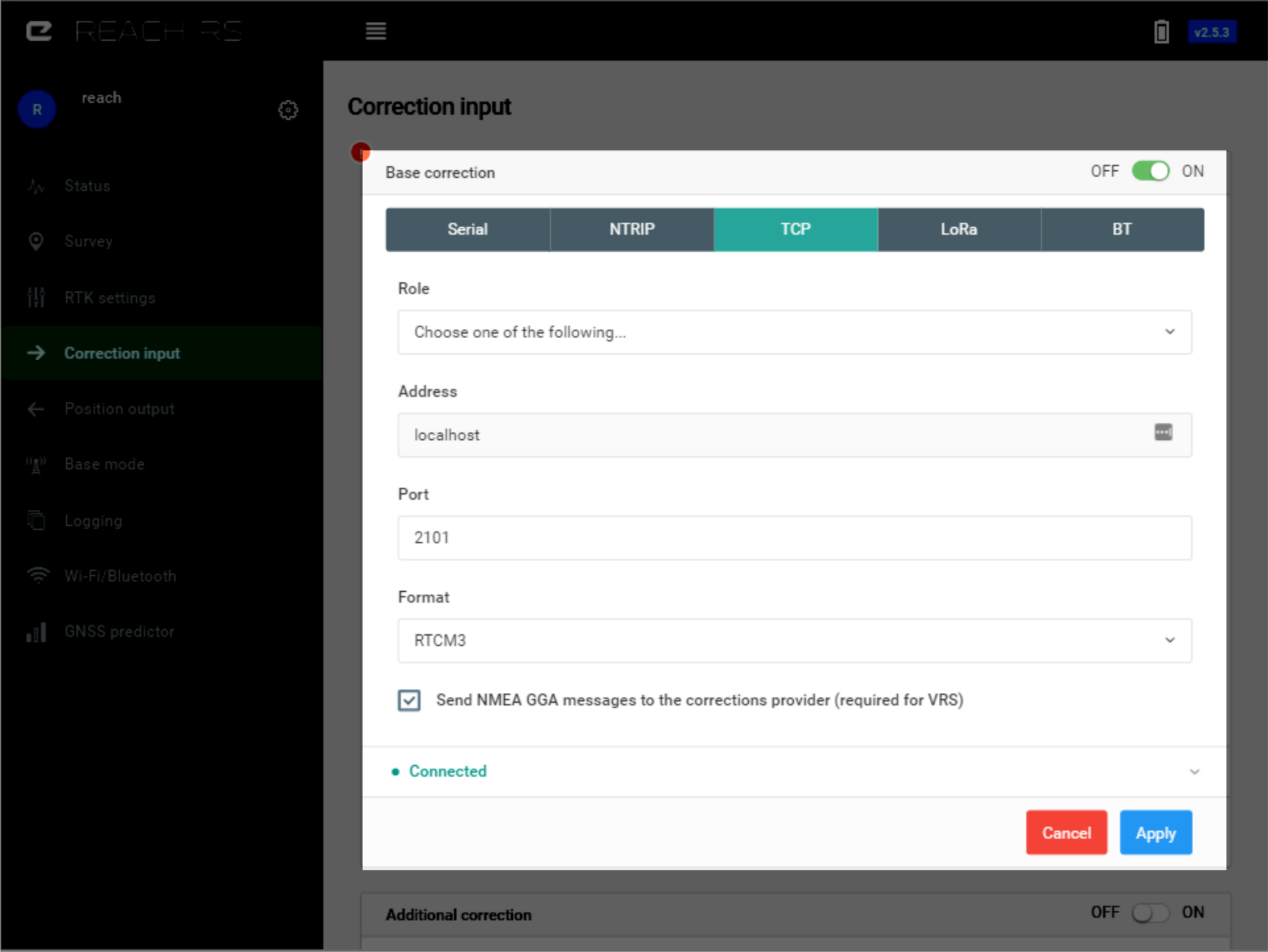
A typical scenario for using TCP correction input is when both the base and the rover are on the same network. Note that when devices are on different networks, you can not send data directly unless public IP addresses are known, and routers are set up for port forwarding. TCP can also be used to send data to or receive from a remote server with a public IP.
note
Ports below 3000 are reserved for internal use only.
TCP supports two roles:
Server#
You need to specify a port, and then clients will be able to connect to this device on it’s IP address. Many clients can be connected to the same server.
Client#
You need to specify IP address of the server and port number.
If Reach Panel does not allow to set a certain port number, it means that it is reserved for internal use.
LoRa Radio#
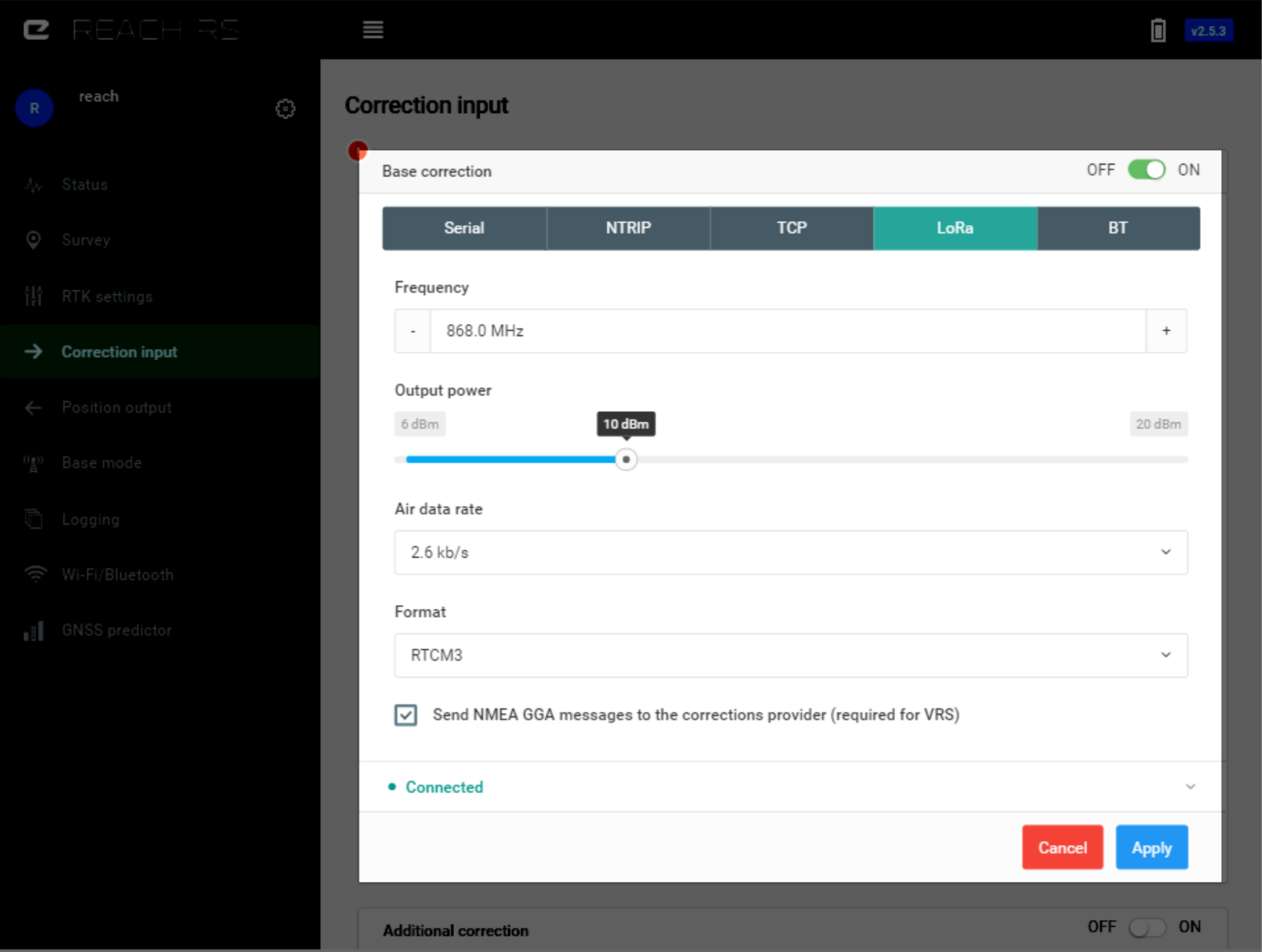
Reach RS/RS+ has internal LoRa radio which is used for receiving or sending corrections. The radio works only in one way, it could either be configured to send corrections (on base) or to receive them (on rover). Using LoRa modulation, it is possible to hit up to 19km (11.8 miles) in line of sight or a few km in urban areas with just 20 dBm power output. As long as frequency and air rate settings match, an unlimited number of rovers can listen for correction from the same base.
Frequency and air rate settings must match what was configured on the base.
Bluetooth#
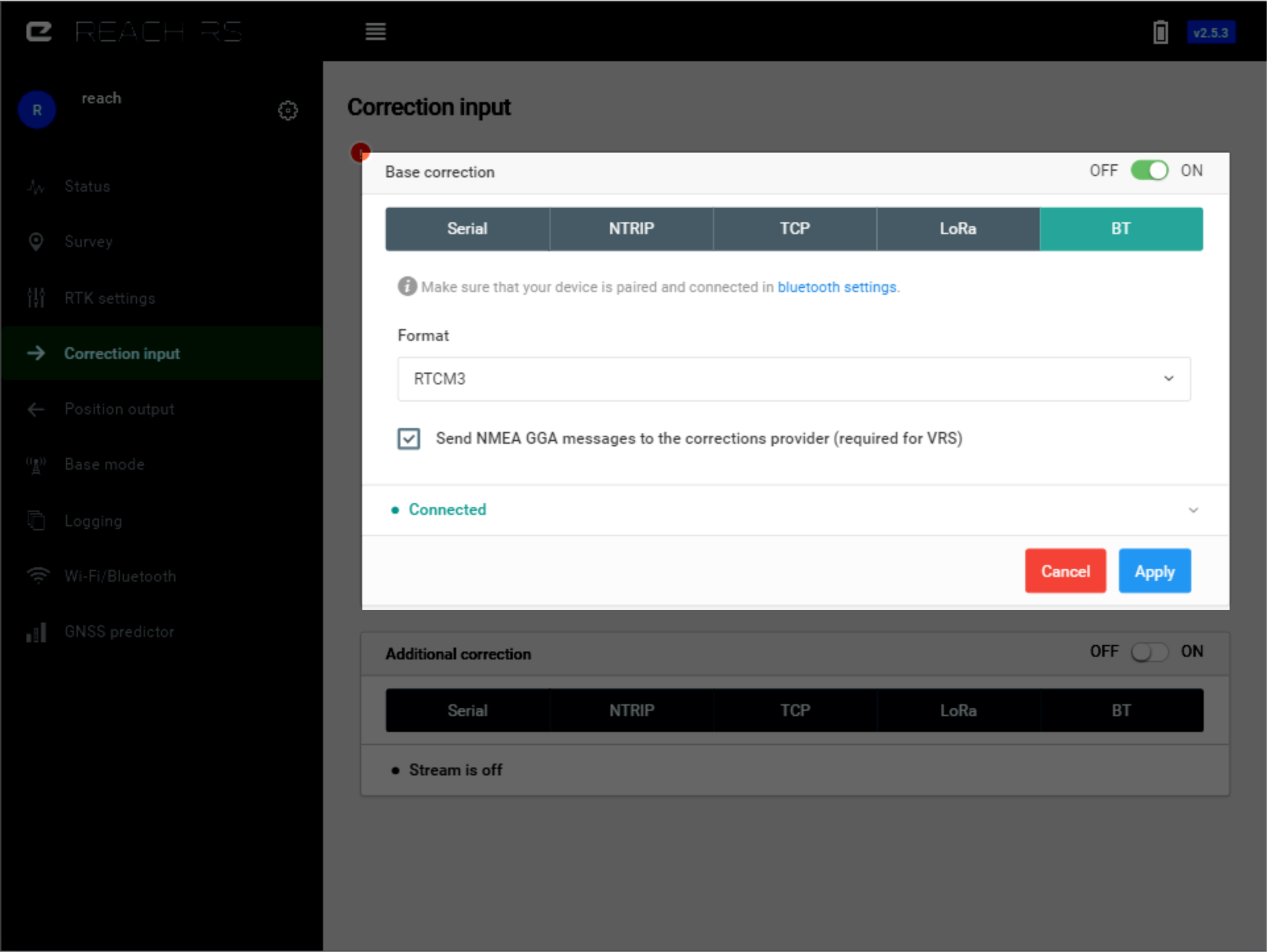
You can use Bluetooth for correction input. For example you can use your phone to pass NTRIP corrections via Bluetooth to Reach. Check out Bluetooth section to learn more about connecting your device via Bluetooth.